XCASCADE (3D)
Versatile tool for modeling X-ray induced irradiation of materials
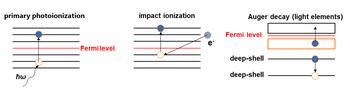
XCASCADE [1,2] is a Monte Carlo (MC) code realizing individual-particle event-by-event MC simulation tool. It simulates X-ray-induced electron cascades in solids, using atomistic approximation. An electron cascade typically starts with an absorption of an X-ray photon, which creates an energetic photoelectron and a valence or inner-shell atomic hole in the target.
In the latter case, the hole then undergoes single- or multiple-step decay (depending on the target and photon energy) creating one or several secondary electrons. Photo- and secondary electrons scatter on atoms inelastically creating more secondary electrons until they can no longer excite more electrons (i.e. their energy falls below the lowest ionization threshold of the target's atoms). It is also possible to start a cascade with an impact electron instead of a photon.
The program implements a “standard” MC algorithm. It does not include the effects such as DOS, correlations, Pauli’s blocking. The solid target is characterized by its atomic composition, density, and energy levels. The laser pulse is characterized by its duration, shape, fluence and photon energy.
[1] N. Medvedev, Appl. Phys. B 118, 417 (2015); Erratum Appl. Phys. B 125, 80 (2019).
[2] B. Ziaja, D. van der Spoel, A. Szoeke, J. Hajdu, Phys. Rev. B. 64, 214104 (2001).
Spatio-temporal modeling of X-ray induced electron cascades in various materials
XCASCADE 3D [2,3] is a Monte Carlo (MC) code based on XCASCADE code, which, in addition to providing temporal information about X-ray-induced free electron cascades, also predicts their spatial evolution. In other words, it provides full spatio-temporal information on free electron density in a target material after its irradiation with X rays.
The solid target is characterized by its atomic composition (determining atomic energy levels, photoabsorption cross sections, elastic/inelastic electron-atom scattering cross sections, Auger decay times), and atomic density. The X-ray laser pulse is characterized by its temporal shape, duration, fluence and photon energy. The code relies on individual particle event-by-event MC approach. Its recent version has been tested in [4] for various materials.
[3] V. Lipp, N. Medvedev, B. Ziaja, Proc. of SPIE 10239, 102360H (2017).
[4] V. Lipp, I. Milov, N. Medvedev, J. Sync. Rad. 29, 323 (2022).
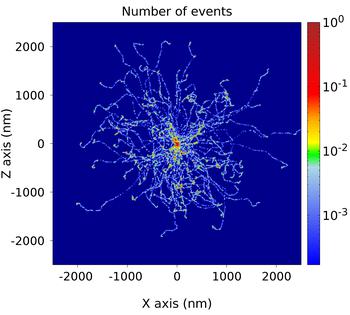
100 electron cascades in LiF, each triggered by an impact of
an 10 keV photoelectron, simulated with XCASCADE 3D code.
License for XCASCADE (3D)
There are two kinds of licenses for XCASCADE (3D), a non-commercial license and a commercial one.
The non-commercial license can be distributed only to group leaders or senior scientists permanently employed in a research institute. They are obliged to use XCASCADE (3D) only: (i) for peaceful and non-commercial purposes, (ii) in science and education, (iii) within the research group specified in the license, and to cite it in the resulting publications. Other conditions of use are specified in the license. The non-commercial XCASCADE (3D) license is for free.
Groups interested in getting an XCASCADE (3D) license can send an email request to our Administrative Assistant, Ms. Berit Heiser:
berit.heiser@desy.de
Please specify the name of the interested group leader and of the research institute clearly in the email. Emails without the (valid) data will not be further processed.